Sterilization
Surgical Castration in Dogs: Benefits, Considerations, and Alternatives
Surgical castration in dogs offers a range of benefits that should be considered when deciding on this procedure. One of the main advantages is population control, as sterilization prevents unwanted reproduction and the proliferation of abandoned animals. Additionally, surgical castration improves the dog’s health by reducing the risk of diseases such as testicular and prostate tumors. Furthermore, by lowering sex hormone levels, castration can also help stabilize behavior reducing aggressive or undesirable behaviors. Neutering your dog is an important decision, but is it the right one for you and your pet?.
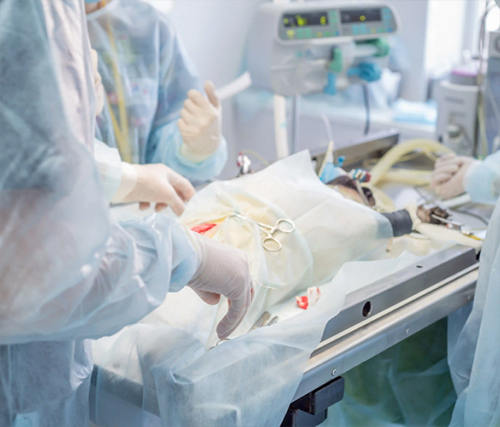
To help you make an informed decision, it i’s essential to understand the benefits of surgical castration, any potential risks related to your dog’s health, behavior, or weight, the appropriate age for the procedure, and its approximate cost. Since any surgical intervention carries potential risks,we encourage you to gather as much information as possible and always consult your veterinarian. This way, you can determine whether surgical castration is the best option for your dog and your family or if you should consider the painless, biological, reversible, and equal alternative available today.

Comencemos:
Surgical castration, sometimes called sterilization, removal of reproductive organs is a common surgical procedure that permanently prevents dogs from reproducing. In male dogs, this is known as castration and involves removing the testicles. In female dogs, the ovaries and usually the uterus are removed, a procedure known as spaying. Both procedures require general anesthesia and post-operative care until the veterinarian determines the dog has fully recovered.
Surgical castration generally costs between 100,000 and over 400,000 Chilean pesos, depending on your dog’s breed, size, and sex.
The cost may vary because:
- Spaying a female is more complex and involves internal organ surgery, making it more expensive than neutering a male.
- Some surgeries are more difficult, such as neutering a male with cryptorchidism (undescended testicle).
- Larger dogs require more anesthesia, and their surgeries take longer due to their size.
While it is not entirely free, some municipalities offer low-cost castration programs as part of their canine population control plans (PTRAC). Additionally, some veterinary charities, NGOs, and rescue organizations may offer free or low-cost sterilization for pet owners.
Although surgical castration is a common procedure, it is still a surgery, and like any surgery, complications are possible. However, the risks are generally low.
During the operation, your dog will be under anesthesia and will receive constant monitoring from the veterinary team to ensure safety. It is crucial that the procedure is performed under general anesthesia with proper pain relief before and after surgery. If you have any concerns, speak with your veterinarian, who can explain the risks and benefits of castration, as well as present the biological, reversible, and equal alternative available today.
The ideal age for surgical castration depends on your dog’s breed, size, and sex. There is ongoing debate about the “best” age, but your veterinarian can guide you based on the latest research and biotechnology.
Most dogs are neutered between six months and two years old. If you want to completely prevent unwanted pregnancies, you can sterilize your dog before reaching sexual maturity. Smaller dogs tend to reach maturity earlier than larger breeds. In some cases, veterinarians may recommend waiting since early castration has been linked to certain health risks in some breeds.
Some veterinarians prefer to spay females before their first heat cycle to reduce the risk of mammary tumors reproductive infections and unwanted pregnancies. Others recommend waiting until after the first heat cycle to allow hormonal development, which may help prevent certain long-term health issues.
So, what is the best option?
According to the British Veterinary Association, “there is currently not enough scientific evidence to take a definitive stance on early castration in dogs.” This means that there is no clear-cut answer as to which method is best.
It is essential to weigh the pros and cons of each approach before making a decision about sterilization. Consulting with your veterinarian will help you choose the most suitable option for your pet’s health and well-being.
There are no known health benefits to allowing a female dog to have a litter before being spayed. Pregnancy and birth can involve complications, and caring for puppies is expensive, time-consuming, and demanding. Breeding should be done responsibly and only after careful consideration
It is essential to weigh the benefits and risks, as well as consult your veterinarian about any concerns. Many pet owners choose surgical castration to prevent pregnancy, control unwanted behaviors, and reduce health risks. However, these benefits should be balanced with potential concerns, such as weight gain, urinary incontinence, coat changes, and breed-specific risks.
Always involve your veterinarian in these discussions, they can provide up-to-date research and information on advanced technologies to minimize risks and maximize benefits. Additionally, consider your dog’s psychological well-being, as anxiety and behavioral changes can also be factors in your decision.
Surgical castration offers the following benefits:





Considerations Before Choosing Surgical Castration
Although surgical castration has many benefits, it may not be suitable for every dog. Here are some important considerations:
- Castration is permanent
- Possible weight gain
- Potential links to other health issues (e.g., anxiety)
- Urinary incontinence risk
- Coat changes

®EGALITTE is the world’s only biopharmaceutical designed for temporary sterilization in both male and female dogs. It offers a painless, biological, reversible, and equitable alternative to traditional sterilization methods, making it a unique and innovative solution in veterinary medicine today.
Always Consult Your Veterinarian
If you’re considering surgical castration for your dog, your veterinarian is the best person to discuss it with. They can provide reliable, research-based information, answer any questions about the benefits and risks, explain the surgical procedure, outline the associated costs, and give you an idea of your pet’s recovery time.
Additionally, your veterinarian can inform you about Egalitte, a biological, reversible, and equitable alternative to temporarily block your pet’s reproductive function.

Frequently Asked Questions About Surgical Castration
Will my dog gain weight after surgical castration?
Yes
Can surgical castration change my dog's behavior?
Yes
Does surgical castration make dogs calmer?
No
Can surgical castration cause urinary incontinence?
Yes
Will surgical castration change my dog’s personality?
Yes
Can my dog participate in shows and competitions after surgical castration?
No
Is There a More Dog-Friendly Alternative?
Yes! In collaboration with the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine of the University of Chile (FAVET), we have developed a biological (immunological), reversible (maintains reproductive potential), and equal (for both male and female dogs) alternative.
Our innovative solution, patented in over 40 countries and available in Chile, is unique in the world. Immunocastration offers an alternative to traditional surgical castration, using the dog’s immune system to suppress reproductive function.
Developed over 15 years of research, this safer and more ethical approach has been tested in multiple countries to improve animal welfare while respecting multi-species family well-being.
Additionally, our work has been featured in reputable publications such as Reuters and VetPracticeMag, showcasing the advancements in immunological sterilization.
Talk to Your Veterinarian: If you a’re considering surgical castration for your dog, the best person to talk to is your veterinarian. They can provide evidence-based advice, answer your questions, explain the procedure and costs, and discuss your dog’s recovery process.
Your veterinarian can also inform you about the biological, reversible, and equal alternative for controlling your dog’s reproductive function.
